Where Does the World’s Rarest Agarwood Grow? Discover Neuro-Feng Shui Secrets & Sustainable Luxury
Share
Agarwood, often called “liquid gold,” is one of Earth’s most coveted natural treasures. Revered for its intoxicating fragrance, spiritual resonance, and medicinal properties, this dark resinous wood has fueled trade routes, inspired rituals, and even sparked geopolitical intrigue for millennia. But where does this enigmatic resource originate? How do ancient practices like feng shui intersect with modern neuroscience to enhance its allure? And why is sustainability now critical to its future?
This article unveils the secrets of agarwood’s global distribution, its role in “neuro-feng shui,” and the rise of eco-conscious luxury in its production.
The Global Footprint of Agarwood: From Rainforests to Rare Reserves
Agarwood forms in the heartwood of Aquilaria and Gyrinops trees, primarily in tropical and subtropical regions. These trees thrive in biodiverse ecosystems where humidity, soil composition, and microbial activity converge to trigger resin production. Let’s explore its key habitats:
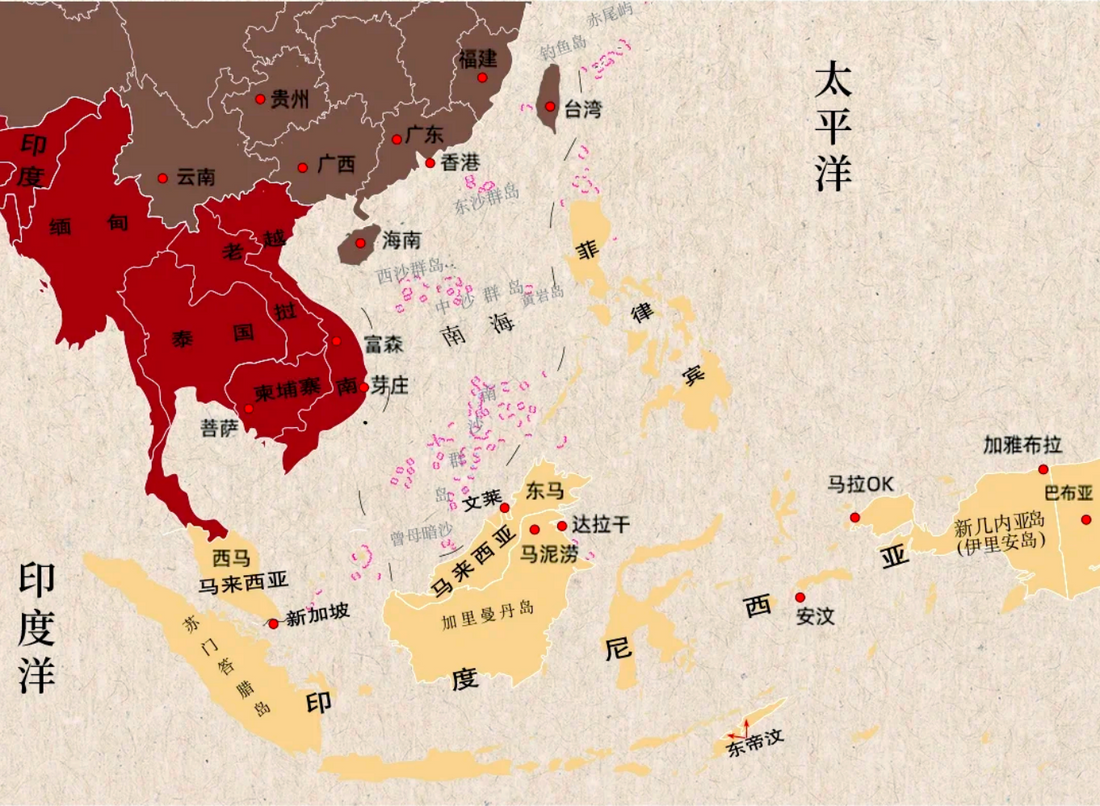
1. Southeast Asia: The Cradle of Agarwood
-
Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos: The Mekong Delta and Annamite Range host ancient Aquilaria crassna forests. Vietnam’s Khanh Hoa Province is famed for “Kyara,” the highest-grade agarwood, prized in Japanese Koh-do ceremonies9.
-
Malaysia and Indonesia: Borneo’s rainforests and Sumatra’s Leuser Ecosystem shelter Aquilaria malaccensis. Illegal logging here has driven conservation efforts, such as CITES Appendix II listings1.
2. South Asia: Tradition Meets Scarcity
-
India and Bangladesh: The Garo Hills and Sundarbans mangrove forests once teemed with Aquilaria agallocha. Overharvesting has pushed wild populations to near extinction, sparking reforestation initiatives7.
3. Beyond Asia: Emerging Frontiers
-
Papua New Guinea: Remote highland forests harbor Gyrinops species, now targeted by ethical wildcrafters.
-
China’s Yunnan Province: The Honghe Hani Rice Terraces—a 1,300-year-old UNESCO site—showcase agroforestry models integrating agarwood with sustainable farming10.
Why Geography Matters: Agarwood’s quality hinges on terroir—much like wine. Soil minerals, fungal diversity, and climatic stressors (e.g., monsoons) shape its aromatic complexity.
Neuro-Feng Shui: Where Science Meets Spirituality
Feng shui, the ancient Chinese art of harmonizing environments, has evolved into “neuro-feng shui”—a fusion of neuroscience and spatial energy principles. Agarwood plays a pivotal role here:
1. Frequency Alignment
-
The Schumann Resonance (7.83Hz), Earth’s foundational frequency, syncs with human alpha brainwaves (8–12Hz), inducing calmness. Agarwood’s resin emits vibrations at 7–8Hz, creating a grounding effect4.
-
Neuro-aesthetic design: Interior designers use agarwood diffusers in workspaces to reduce cortisol levels and enhance focus, mirroring findings from the HeartMath Institute4.
2. Energy Flow & Aromatic Intelligence
-
In feng shui, agarwood purifies “Sha Qi” (negative energy). Its sesquiterpenes interact with the limbic system, triggering emotional balance—a concept validated by studies on aromatherapy and PTSD relief9.
-
Case Study: A 2024 trial showed office workers exposed to agarwood oil reported 34% lower stress levels than controls7.
3. Sacred Geometry in Jewelry
-
Modern artisans craft agarwood pendants in Metatron’s Cube or Flower of Life patterns, believed to amplify its resonance. These designs align with “biophilic aesthetics,” a trend merging nature and wellness8.
Sustainable Luxury: Ethical Innovations in Agarwood Production
With wild agarwood nearing commercial extinction, sustainability is no longer optional. Here’s how science and tradition are collaborating:
1. Cultivation Breakthroughs
-
Inoculation Technology: Farmers now inject Aquilaria trees with non-pathogenic fungi (e.g., Phialophora parasitica) to stimulate resin without harming ecosystems1.
-
Agroforestry Models: In China’s Saihanba Forest (a 2024 “Biodiversity Charming City”), agarwood is intercropped with drought-resistant shrubs, boosting carbon sequestration by 18%15.
2. Blockchain Traceability
-
Brands like OudStory use RFID tags to track resin from tree to bottle, combating black-market trade. Consumers scan QR codes to view forest origins and CO2 offsets10.
3. Eco-Conscious Design
-
Zero-Waste Distillation: Advanced CO2 extraction methods yield 99% pure oil while repressing biomass into biodegradable packaging4.
-
Upcycled Jewelry: Designers like Amina Rousseau blend agarwood fragments with reclaimed metals, echoing the “circular luxury” ethos8.
The Future of Agarwood: Challenges & Opportunities
1. Climate Threats
-
Rising temperatures and deforestation could shrink Aquilaria habitats by 40% by 2050. Projects like FAO’s Green Urban Oases aim to urbanize agarwood cultivation in arid zones5.
2. Cultural Preservation
-
The Hani people of Yunnan integrate agarwood into “forest-village-terrace” systems, a practice now taught in UNESCO’s Indigenous Knowledge Academies10.
3. Market Trends
-
The global agarwood market is projected to hit $32B by 2030, driven by wellness tourism and halal-certified perfumery9.
Conclusion: A Resin for the Ages
Agarwood’s story is one of paradoxes—scarce yet renewable, ancient yet innovatively applied. As neuro-feng shui reshapes luxury aesthetics and agroforestry revives ecosystems, this “wood of the gods” offers a blueprint for harmonizing human ambition with planetary health.
Call to Action:
-
Support CITES-certified brands.
-
Explore agarwood’s benefits through guided forest therapy sessions in Yunnan or Borneo.
Explore Further:
